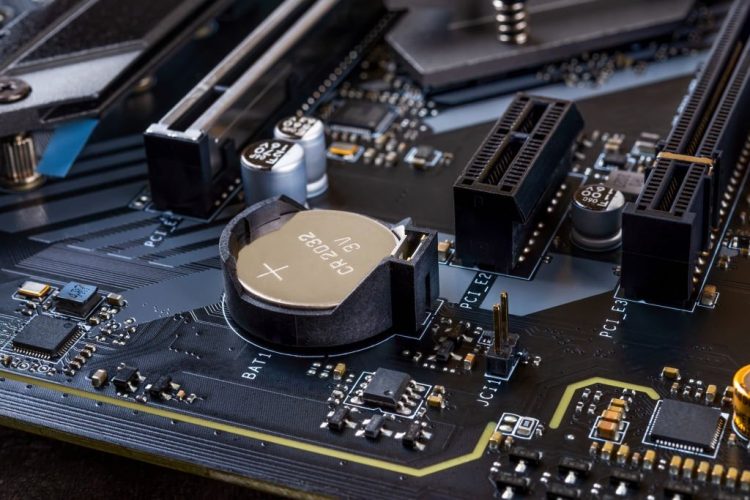
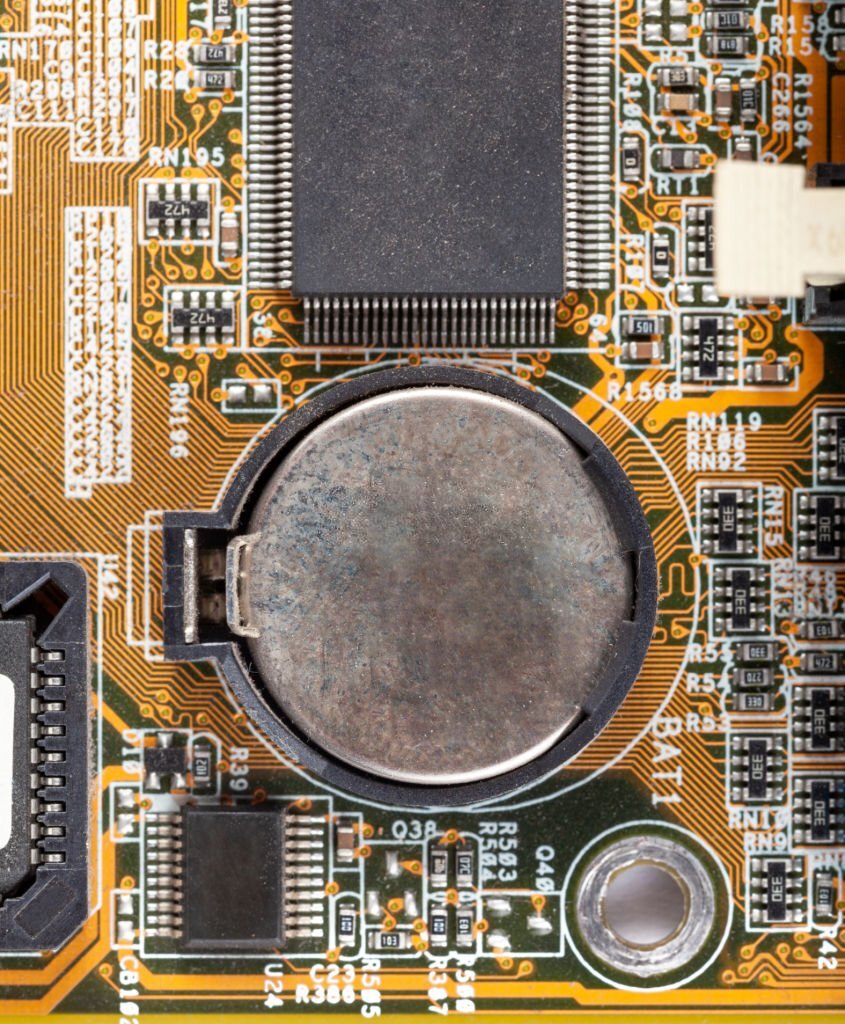
The term CMOS is an acronym for Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor. A lithium battery the size of a coin serves as the CMOS battery and powers the CMOS RAM.
The fundamental PC hardware parameters, such as the date and time, are stored in the CMOS RAM.
A few examples of BIOS settings include plug-and-play information, RAM amount and type, CPU type, and speed.
The CMOS RAM needs to be powered because it is volatile (all RAMS lose data when the power is cut off).
Because of this, your PC—desktop or laptop—needs a CMOS battery.
Typical Symptoms of a CMOS Battery Failure
Failure of the CMOS battery can lead to a variety of computer problems.
The laptop or computer’s capacity to perform is impacted when the battery dies since it is unable to recognize the device drivers.
Fortunately, there are clear indications that a CMOS battery is failing. You can properly fix and replace it before a problem emerges if you can see the problems as we go over them below.
The following are signs of a failing CMOS battery:
- The laptop has trouble starting up.
- A continuous beeping sound is coming from the motherboard.
- The time and date keep on resetting.
- Peripherals are either unresponsive or respond incorrectly.
- Hardware drivers are no longer available.
- Internet browsing is not accessible.
1. The Time And Date Keep Resetting
The frequent resetting of the date and time is a common sign of CMOS battery failure. The date and time keep resetting no matter how many times you adjust them.
Every time you shut down the device, it resets because if the battery dies, it can no longer set the correct date and time.
Even if you enter the right time and date in the BIOS settings, the time and date will reset. By default, it will reset both the time and the date.
If you have noticed this, there’s a good possibility the CMOS battery is dead and you need to get a new one right away.
2. Drivers Not Responding and Various Hardware Failures
Unusual hardware faults and drivers that are no longer responsive are other important indicator that the CMOS battery is deteriorating.
The primary functions of the CMOS battery are to store BIOS configurations and maintain a log of the hardware drivers that your system employs.
The computer can no longer recognize some of its hardware due to the unresponsive drivers when the CMOS battery is likely to die.
Hardware anomalies may suddenly appear as a result of this. In some cases, you may come across a corrupt BIOS on your laptop.
3. Keyboard Acting Weird
The peripheral keys are not responding. The keyboard is no longer accepting keyboard inputs, and the pointer is not moving.
Alternately, the OS may only respond to your key inputs if the peripheral keys appear to be out of alignment and the cursor is acting strangely.
A customized keyboard setup that abruptly returns to its default setting is another warning indication. These are all warning signals that a CMOS battery is failing.
4. Checksum Error
Checksum Error or a reading error, while your laptop or computer is loading up, is another crucial indicator of CMOS battery failure.
It happens when the PC boots up and the BIOS and CMOS clash. When this occurs, the computer can either no longer read start-up information or the information does not match the BIOS.
The eros displays while the machine is booting because your PC cannot check the values without the CMOS battery.
5. Random Shutdowns and Booting Issues
Does your computer cut off without warning, freeze, or have problems starting up? Therefore, it might be a sign of a dying CMOS battery.
The drivers have ceased responding while the PC is running, causing your computer to crash.
On the other side, because the hardware drivers don’t function properly, a CMOS battery failure can also result in booting issues.
Booting errors are brought on by non-responsive device drivers, which are in charge of initiating a computer’s startup.
6. Constant Beeping Noise and No Internet Connection
Does your motherboard make noise all the time? Your CMOS battery needs to be replaced if you hear a continuous beeping sound coming from the hardware.
Internet connection loss is another common symptom.
The PC may be unable to connect to the internet if the CMOS battery is dead or nearly dead because the BIOS is forced to keep track of drivers and hardware problems.
CMOS Battery Removal and Replacement Instructions
Let’s take out that annoying CMOS battery and put in a fresh one. It’s a rather easy process. You will simply require a few materials:
- Screwdriver
- Squeezing air
- a fresh CMOS battery
- ESD pad
A brand-new CMOS battery can be purchased online at a very affordable price, typically between $1 and $10.
1. Find a good working space
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a threat to your laptop’s internal parts. Work on a non-carpeted surface to prevent building up a charge.
Use a hard, flat surface for your work. Working on a conductive foam pad is actually preferable if it’s possible. With these pads, ESD will be avoided.
There’s a chance that your hands have static electricity. To discharge the charge before you begin working, rub your hands on a metal surface.
For this DIY project, you should probably wear an anti-static wristband if you have one.
2. Disconnect everything
Unplug your computer from the power source and shut it down. Remove all wires from the laptop, including those from any peripheral devices.
3. Remove the casing
Turn the computer over. The screws holding the laptop case in place can be removed with the screwdriver. Once the casing has been unscrewed, remove it.
Be aware that some laptops just have one sizable case that needs to be taken off. Other laptops have a number of smaller casings that provide access to various computer parts.
Unscrew all the casings and have a look around if you are unsure of which one allows you access to what,
Have a few small bowls on hand to hold the screws you remove.
Don’t let them roll off the table and go lost because you’ll need to find them all when it’s time to put them back in.
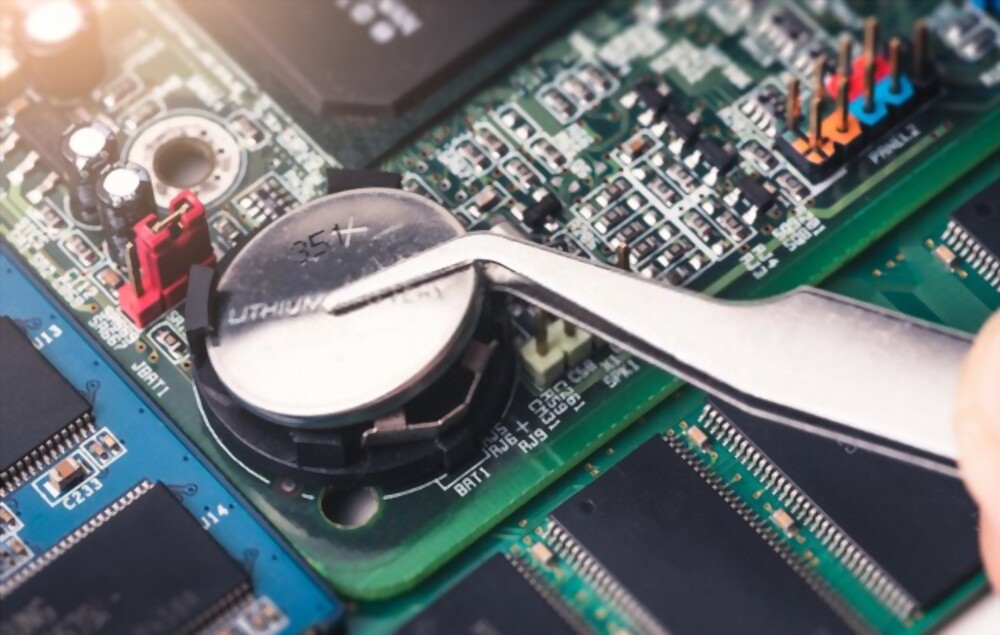
4. Remove CMOS Battery
You ought to now be able to see the motherboard. When working around the motherboard, use extreme caution. Your computer’s most crucial piece of hardware is located here, and damaging it could cause catastrophic harm to your laptop.
The round, glossy CMOS battery is visible. It usually rests inside a tiny retaining socket and resembles a button or coin.
Like the batteries in your mouse, the CMOS battery pulls out of the socket to be removed.
Observe the battery’s orientation before removing it so you will know which direction to insert the new one.
5. Insert the new CMOS battery
In the same spot, install the new battery. Make sure the new battery is positioned in the same way as the old one.
6. Close the casing
Reinstall the screws on each of the computer’s shells. Install the battery again. Swap out the outer case.
7. Test the laptop
Reconnect your laptop to its power supply and turn it on. Don’t panic if the date and time are still off or if drivers are missing; BIOS should have returned to its default settings.
The time must be reset, and the drivers must be installed again.
Important Facts to Keep in Mind Regarding the CMOS Battery
- Avoid recharging or burning waste.
- Keep in a dry, cold environment.
- The battery should be inserted correctly.
- Before using the battery, clean it.
- Dispose of the batteries properly.